Diffraction Vs Refraction - Resolution and Diffraction Gratings : This is a simulation of a typical laser diffraction lab set up.
Diffraction involves a change in direction of waves as they pass through an opening or around a barrier in their path. The pattern has maximum intensity at θ = 0, and a series of peaks of decreasing intensity. Use the checkbox to place the grating in front of the laser, and look at the pattern of dots that appear on the screen. The third type of light behavior is refraction. This complementary, or dual, role for the behavior of light can be employed to describe all of the known characteristics that have been observed experimentally, ranging from refraction, reflection, interference, and diffraction, to the results with polarized light and the photoelectric effect.
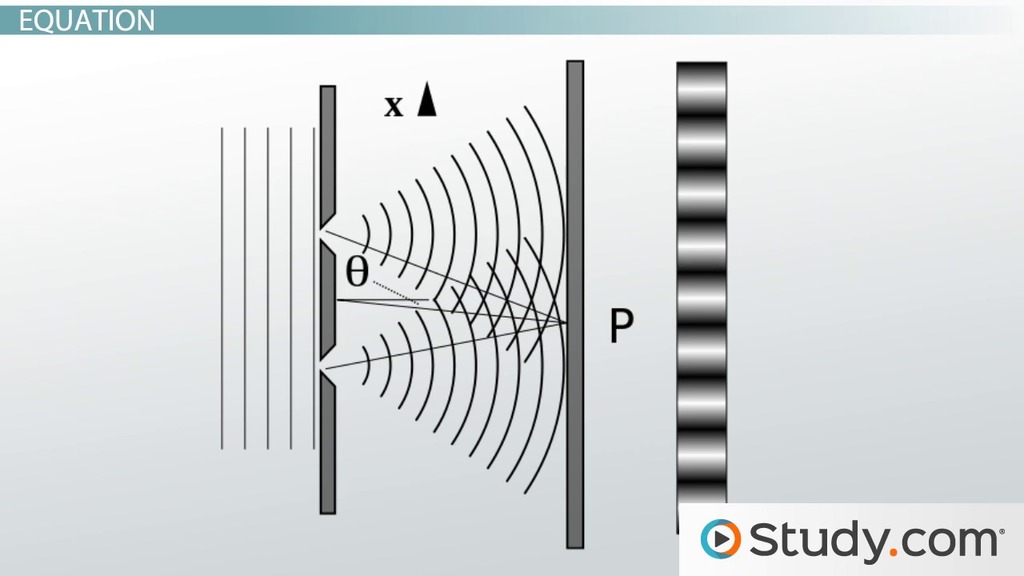
Diffraction spreads out light waves;
This is a simulation of a typical laser diffraction lab set up. Reflection, refraction and diffraction are all boundary behaviors of waves associated with the bending of the path of a wave. The angle, α, subtended by these two minima is given by: Use the checkbox to place the grating in front of the laser, and look at the pattern of dots that appear on the screen. Diffraction involves a change in direction of waves as they pass through an opening or around a barrier in their path. In that unit, we saw that water waves have the ability to travel around corners, around obstacles and through openings. Like any wave, a sound wave doesn't just stop when it reaches the end of the space through which it is traveling or when it encounters an obstacle in its path.rather, a sound wave will undergo certain behaviors when it encounters the end of the space or an obstacle. Refraction definition, the change of direction of a ray of light, sound, heat, or the like, in passing obliquely from one medium into another in which its wave velocity is different. It is defined as the bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The third type of light behavior is refraction. May 17, 2016 · at times light behaves as a particle, and at other times as a wave. Behavior of sound waves reflection, refraction, and diffraction. This should not lead you to think that larger apertures are better, even though very small apertures create a soft image;
Refraction is where light waves pass through a material (what scientists call a medium ) and change direction. In that unit, we saw that water waves have the ability to travel around corners, around obstacles and through openings. Reflection, refraction and diffraction are all boundary behaviors of waves associated with the bending of the path of a wave. The diffraction of water waves was discussed in unit 10 of the physics classroom tutorial. This is a simulation of a typical laser diffraction lab set up.

Like any wave, a sound wave doesn't just stop when it reaches the end of the space through which it is traveling or when it encounters an obstacle in its path.rather, a sound wave will undergo certain behaviors when it encounters the end of the space or an obstacle.
The angle, α, subtended by these two minima is given by: Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or opening. Behavior of sound waves reflection, refraction, and diffraction. This complementary, or dual, role for the behavior of light can be employed to describe all of the known characteristics that have been observed experimentally, ranging from refraction, reflection, interference, and diffraction, to the results with polarized light and the photoelectric effect. Diffraction spreads out light waves; Most of the diffracted light falls between the first minima. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a secondary source of the propagating wave. Examine the set up in the 3d window, it shows a laser, a diffraction grating, and a screen. Diffraction of sound waves and of light waves will be discussed in a later unit of the physics classroom tutorial. An example of this is water vapor in the air diffracting light from the sun to create a rainbow. Use the checkbox to place the grating in front of the laser, and look at the pattern of dots that appear on the screen. Most lenses are also quite soft. Diffraction involves a change in direction of waves as they pass through an opening or around a barrier in their path.
An example of this is water vapor in the air diffracting light from the sun to create a rainbow. May 17, 2016 · at times light behaves as a particle, and at other times as a wave. Diffraction spreads out light waves; The third type of light behavior is refraction. This should not lead you to think that larger apertures are better, even though very small apertures create a soft image;

Behavior of sound waves reflection, refraction, and diffraction.
May 17, 2016 · at times light behaves as a particle, and at other times as a wave. Reflection, refraction and diffraction are all boundary behaviors of waves associated with the bending of the path of a wave. The angle, α, subtended by these two minima is given by: Most of the diffracted light falls between the first minima. The pattern has maximum intensity at θ = 0, and a series of peaks of decreasing intensity. Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or opening. Refraction definition, the change of direction of a ray of light, sound, heat, or the like, in passing obliquely from one medium into another in which its wave velocity is different. This is a simulation of a typical laser diffraction lab set up. The third type of light behavior is refraction. An example of this is water vapor in the air diffracting light from the sun to create a rainbow. Diffraction spreads out light waves; Like any wave, a sound wave doesn't just stop when it reaches the end of the space through which it is traveling or when it encounters an obstacle in its path.rather, a sound wave will undergo certain behaviors when it encounters the end of the space or an obstacle. Examine the set up in the 3d window, it shows a laser, a diffraction grating, and a screen.
Diffraction Vs Refraction - Resolution and Diffraction Gratings : This is a simulation of a typical laser diffraction lab set up.. Refraction is where light waves pass through a material (what scientists call a medium ) and change direction. This is a simulation of a typical laser diffraction lab set up. Diffraction involves a change in direction of waves as they pass through an opening or around a barrier in their path. In that unit, we saw that water waves have the ability to travel around corners, around obstacles and through openings. Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or opening.
Diffraction refers to various phenomena that occur when a wave encounters an obstacle or opening diffraction. Refraction definition, the change of direction of a ray of light, sound, heat, or the like, in passing obliquely from one medium into another in which its wave velocity is different.
Post a Comment for "Diffraction Vs Refraction - Resolution and Diffraction Gratings : This is a simulation of a typical laser diffraction lab set up."